Female Metabolism: How It Changes With Age and Weight Loss
Metabolism is one of the most misunderstood parts of women’s health. Many women in their 30s, 40s, or 50s notice that weight loss becomes harder, energy levels drop, and their bodies respond differently to food and exercise.

The reason isn’t just “getting older” — it’s a combination of hormonal changes, muscle loss, and metabolic adaptation unique to women. Let’s dive into how female metabolism changes with age and weight loss, and how you can keep it strong at every stage of life.
What Is Metabolism and Why It Matters for Women
How Metabolism Works in the Female Body
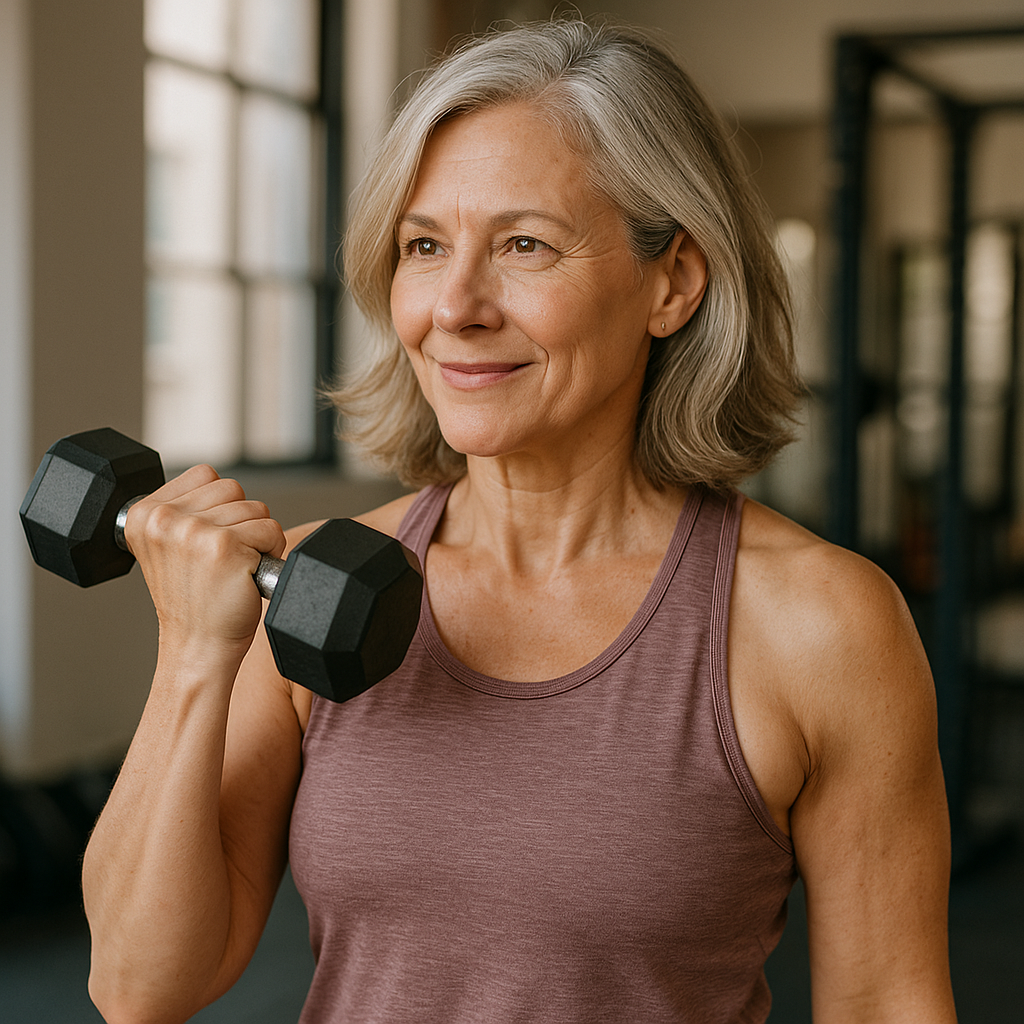
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes your body uses to convert food into energy. It determines how efficiently your body burns calories at rest — known as Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR).
For women, metabolism is closely linked to hormones, reproductive health, and muscle mass. These factors shift dramatically with age, leading to slower fat burning and easier fat storage, especially around the belly and hips.
The Unique Metabolic Traits of Women
The Role of Estrogen and Progesterone
Estrogen supports lean muscle and fat distribution in the hips and thighs, while progesterone helps regulate appetite and mood. When these hormones fluctuate — during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause — your metabolic rate can rise or fall temporarily.
Why Women Store Fat Differently Than Men
Women naturally have more body fat than men for reproductive and hormonal balance. This extra fat acts as a backup source of energy during pregnancy or periods of stress, but it also makes fat loss more challenging — especially post-40.
How Female Metabolism Changes With Age
In Your 20s: Building Metabolic Foundation
Your 20s are your metabolic peak. Hormones, energy, and muscle mass are at their highest, making it easier to maintain or Lose Weight. However, poor diet or overtraining can disrupt thyroid function early on.
In Your 30s: Subtle Slowdown Begins
In your 30s, muscle mass starts to decline if you’re not strength training. Busy careers, motherhood, and stress can elevate cortisol — a hormone that encourages fat storage around the belly.
In Your 40s and 50s: Menopause and Metabolic Drop
During perimenopause and menopause, estrogen levels plummet, leading to reduced muscle, lower calorie burn, and a slower metabolism. Fat redistributes from the thighs and hips to the abdomen, creating the notorious “menopause belly.”
After 60: Slower Digestion and Recovery
As muscle declines further and digestion slows, calorie needs decrease. But metabolism doesn’t stop — it just becomes more sensitive to food choices and movement.
Metabolism and Weight Loss: Why It Gets Harder With Age
Muscle Loss and Resting Metabolism
Muscle is metabolically active — it burns calories even at rest. With aging, sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) causes a drop in resting metabolism. Without resistance training, your body burns fewer calories daily.
Insulin Resistance and Hormone Imbalance
Hormonal changes can cause insulin resistance, making your body store fat more easily and crave sugar. Balancing protein and carb intake helps improve insulin sensitivity.
The Stress Connection: Cortisol and Midlife Weight Gain
Chronic stress raises cortisol, which tells your body to hold on to fat — especially around the waistline. Even with a calorie deficit, stress can block fat loss if cortisol remains high.
How to Boost Female Metabolism Naturally
Eat Smart: Macronutrient Balance for Women
-
Protein: Build muscle and boost thermogenesis (burning calories through digestion).
-
Healthy fats: Support hormones — include avocado, nuts, olive oil.
-
Fiber-rich carbs: Balance blood sugar and digestion (quinoa, oats, beans).
Aim to eat small, nutrient-dense meals every 3–4 hours to keep energy and metabolism steady.
Exercise: The Ultimate Metabolism Booster
-
Strength training (3–4 times per week): Preserves lean muscle mass.
-
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training): Efficiently burns calories and boosts post-workout metabolism.
-
Active lifestyle (NEAT): Walking, stretching, and daily movement burn more calories cumulatively than gym time alone.
💡 Tip: Women who lift weights consistently burn up to 10% more calories at rest than those who only do cardio.
Sleep, Hydration, and Recovery
Sleep deprivation elevates cortisol and hunger hormones (ghrelin), while lowering satiety hormones (leptin).
Aim for:
-
7–9 hours of quality sleep
-
Hydration: Drink half your body weight in ounces daily
-
Recovery days: Allow your metabolism to rest and rebuild muscle tissue
Metabolic Myths Every Woman Should Know
| Myth | Truth |
|---|---|
| Starving helps you lose weight | It lowers metabolism and increases cortisol. |
| Women should eat less as they age | They should eat smarter — with more protein and fiber. |
| Men have faster metabolism because they’re lucky | It’s due to higher muscle mass, not luck. |
| Cardio is the best fat burner | Strength + cardio + nutrition = optimal fat loss. |
Signs of a Sluggish Metabolism
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Weight gain despite healthy habits
-
Cold hands and feet
-
Dry skin or hair loss
-
Sugar cravings and low energy
-
Difficulty losing belly fat
If you notice these, check for thyroid issues, low iron, or hormone imbalances.
FAQs About Female Metabolism
1. At what age does a woman’s metabolism slow down?
Metabolism begins to decline gradually in the late 20s and becomes more noticeable after 40.
2. Can you speed up metabolism after menopause?
Yes. Through strength training, balanced nutrition, and sleep optimization.
3. How much does muscle affect metabolism?
Each pound of muscle burns about 6–10 extra calories per day at rest — small but impactful over time.
4. Does intermittent fasting work for women?
It can, but prolonged fasting may disrupt hormones in some women. Personalized schedules work best.
5. Can stress slow metabolism?
Yes — cortisol suppresses thyroid function and promotes fat storage.
6. Do metabolism boosters work?
Natural methods (exercise, protein, hydration) are far more effective and sustainable than supplements.
Conclusion: Working With, Not Against, Your Metabolism
Your metabolism isn’t broken — it’s adaptive. As a woman, it shifts with every stage of life, reflecting your body’s hormonal and nutritional needs.
Instead of fighting it, learn to work with it:
-
Build muscle
-
Manage stress
-
Sleep deeply
-
Eat real, balanced foods
By aligning with your body’s biology, you’ll not only boost fat loss but also regain energy, confidence, and control over your health.
👉 Learn more from Harvard Health – How Metabolism Changes With Age.


